187 9245 6795
Email: mh_elec@126.com or jacky@mh-elec.com

Low Light Level Image Intensifier, also known as Low Light Level Image Tube, is the core device of low light night vision device and plays a decisive role in the imaging quality of the whole system.
Composition Structure Editing Broadcast
The low-light image intensifier is the core component of the low-light night vision system. The entire low-light night vision system includes an optical imaging lens group, a low-light image intensifier, and a post-processing system. Among them, the low-light image intensifier is the most important part [1]. So far, there have been one generation of low-light image intensifiers, two generations of low-light image intensifiers, three generations of low-light image intensifiers and four generations of low-light image intensifiers. Different generations of low-light image tubes have different structures, but mainly include the following parts: Photocathode, Ion Barrier Film, Micro Channel Plate and Fluorescent Screen. The whole tube is a vacuum device.
Gen 1st
In 1955, A. Sommer discovered a NaKSb(Cs) triple photocathode with high quantum efficiency, which has a good spectral response from visible light to near-infrared, making high-efficiency photoelectric conversion possible under low illumination. At the same time, the concentric sphere electron optical system researched by P. Schangen in the early 1950s and the fiber optic panel invented by E. E. Sheldon in 1958 laid the technical foundation for the enhancement of electronic signals. In the mid-1960s, a cascaded image intensifier coupled with a high-efficiency photocathode and an optical fiber panel came out, known as the first generation of low-light image intensifier (generation tube). In practical application, three tubes need to be cascaded together. As soon as it appeared, it became the focus of development in the field of night vision, gradually replacing the earlier application of active infrared night vision technology [2] . In 1966, the U.S. military began to use it in the Vietnam War. In 1970, it began mass production and equipped troops.
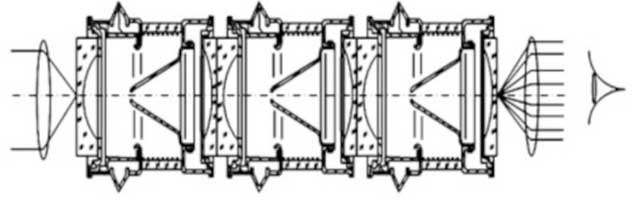
Generation 2nd
The second-generation low-light image intensifier (second-generation tube) was developed in the early 1970s. Its main technical feature is the invention of the microchannel plate and its introduction into the single-stage low-light image tube. The second-generation low-light image intensifiers have two structures: electrostatic focusing type, as shown in Figure 1, and double close-focus focusing thin-film type (referred to as close-up type). It consists of a multi-alkali photocathode, an electron optical system, a microchannel plate (MCP) and a phosphor screen. Many technologically advanced countries such as the United States, Germany, France, Britain, the Netherlands, and Israel can produce second-generation products. Since the 1980s, these countries have basically replaced first-generation products with second-generation products. my country can also produce second-generation and even super second-generation products.
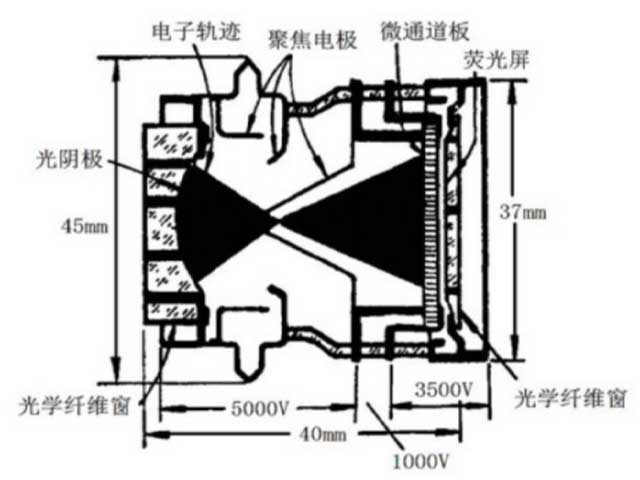
Gen 3
The development of gallium arsenide negative electron affinity (NEA) photocathode has triggered a huge revolution in the low-light field. The salient feature of this type of III-V semiconductor photocathode is its high sensitivity, which can meet the corresponding infrared band through the cathode material composition and structure design. The double proximity structure composed of transmissive GaAs photocathode, long-life, low-noise micro-channel plate and fluorescent screen with aluminum oxide anti-ion feedback film is the third-generation low-light image intensifier (third-generation tube), As shown in Figure 3. Compared with the second-generation tube, the sensitivity of the third-generation tube is increased by 4-8 times, the life span is extended by more than 3 times, and the utilization rate of the night starlight spectrum is significantly improved. The third-generation product began to be researched in the early 1970s, and the US military began to equip troops in the 1980s. The third-generation products developed by the United States are limited to sales to NATO, South Korea, Japan, Israel and Australia.
The third-generation low-light image intensifiers feature GaAs photocathodes and microchannel plates with anti-ion feedback membranes. The anti-ion feedback film can prevent positive ion feedback, reduce the bombardment of the feedback ions on the photocathode, and prolong the life of the photo tube, but at the same time, it also reduces the signal-to-noise ratio and resolution of the photo tube to a certain extent.
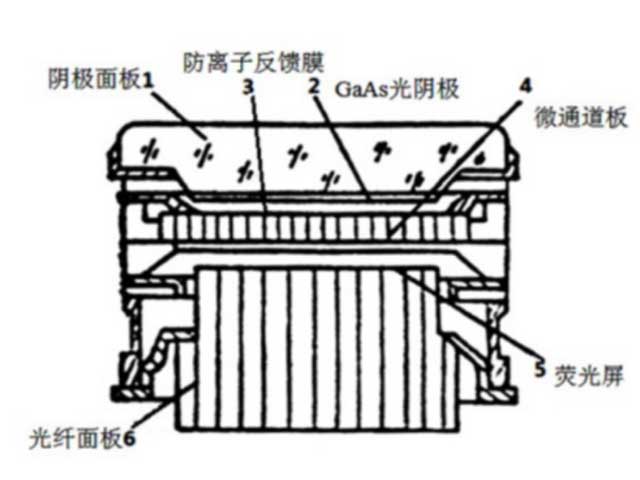
Gen 4th
In the late 1990s, the American ITT Night Vision Company and Litton (Litton) Electro-optic System Company proposed the fourth-generation low-light image intensifier (fourth-generation tube). In 1997, the Department of the Army funded the above two companies with the same funds to start research on this work. At the beginning of 1998, Litton successfully developed the sample tube of the fourth-generation low-light image intensifier whose working life was equivalent to that of the standard third-generation tube (10,000 hours). At the end of 2000, it passed the qualification inspection test of the US Army. The main feature of the fourth-generation tube is the use of a new high-performance micro-channel plate without a membrane and an automatic gating power supply with front proximity. More than 20 years ago, the idea of using bulk conductive glass material to make MCP was proposed, but it was not realized due to the chemical characteristics of the material and the limitations of the glass forming process. According to reports, until the end of the 20th century, research in the United States showed that phosphoric acid glass can meet the requirements of bulk conductive glass MCP.
The structure of the fourth-generation low-light image intensifier is basically the same as that of the third-generation low-light image intensifier. Generally speaking, the two biggest features of the fourth-generation low-light image intensifier are bulk conduction MCP and automatic pulse-gated power supply. The MCP of the fourth-generation low-light image intensifier has reached the technical level of no membrane but can prevent ion feedback. The use of bulk conductive materials greatly reduces ionic feedback, making IBF unnecessary. This increases the signal-to-noise ratio and improves image quality. The fourth-generation low-light image intensifier has a high signal-to-noise ratio, and the detection distance and resolution are much improved compared to the third-generation. The image is quite clear.
Development status of low-light image intensifier tubes
The countries with the most active research on low-light image intensifier technology and the leading production level are the United States and Russia. Their research results on the sensitivity, resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of low-light image intensifiers have made important contributions to the upgrading of low-light night vision technology in the world. In terms of the production of image intensifiers, companies represented by ITT Corporation in the United States mainly research and produce third-generation and ultra-three-generation low-light image intensifiers. They have developed Omlibus III, Omlibus IV and Omlibus V on the basis of the third generation Three-generation low-light image intensifiers; companies represented by DEP in the Netherlands and Philips in France mainly produce ultra-second-generation, high-performance low-light image intensifiers, which are based on the third-generation image intensifier GaAs photocathode materials, processes and theories. Photocathode structure, activation process, etc., launched a series of super second-generation, high-performance image intensifiers such as SHD-3TM, XD-4TM and XR5TM. These high-performance image intensifiers represent the leading level of night vision technology in the world today.
China's low-light night vision technology started in the 1960s and has developed rapidly in the past 50 years. It has initially possessed the ability to generate first-generation, second-generation, and super-second-generation low-light image intensifiers. The research level of China's third-generation low-light image intensifier has also reached the level of the American standard third-generation image intensifier. However, due to the late start of low-light night vision technology in China, there is still a big gap with the advanced level of foreign countries. The main manifestations are: relatively weak in the basic theory and process research of low-light night vision technology; lagging behind the level of advanced countries in low-light equipment manufacturing. Therefore, it is necessary to make efforts in the exploration of low-light key materials, the research on infrared conversion low-light image intensifiers, and the development of high-performance ultraviolet image intensifiers, highlighting technological innovation, promoting high-speed leap-forward development, and greatly enhancing the development of image intensifier technology. development efforts, thereby gradually shortening the gap with foreign advanced levels.
Engineer Manager Name: Jacky
WhatsApp/ Wechat: 0086-187 9245 6795
Email: mh_elec@126.com or jacky@mh-elec.com
 tel
tel



