The principle of low-light night vision image intensifier
2022-04-01

Low-light image intensifiers, also known as low-light image tubes, are the core components of low-light night vision devices and play a decisive role in the imaging quality of the entire system. So far, there have been a generation of low-light image intensifiers, a second-generation low-light image intensifier, a third-generation low-light imagr intensifier, and fourth-generation low-light image intensifier.
Hoe low-light image intensifiers work
The low-light image intensifiers is a photoelectric vacuum imaging device that can enhance the weak light image. It is the core device of various advanced low-light night vision devices. It usually adopts the structure shown in the figure below, mainly composed of photocathode, electronic optical system and fluorescent screen.
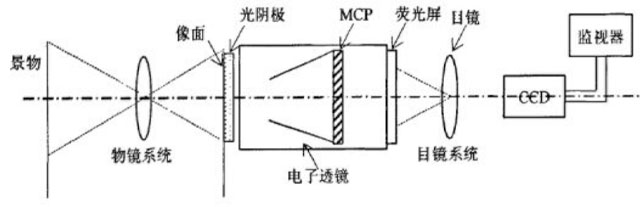
The working principle of the low-light image intensifier: under the illumination of weak light, through the photon-electron conversion of the photocathode, the acceleration and concentration of the electron optical system, and the electron-photon conversion of the phosphor screen, Z eventually makes the originally weak or invisible light. The signal becomes a stronger visible light signal.
1. Photon-electron conversion
The low-light image intensifier uses the external photoelectric effect of the photocathode to convert the input weak light signal into an electronic signal. The photocathode is made of photosensitive material. Under the illumination of weak light, the weak or invisible light is collected on the photosensitive surface by the optical system, and the photoelectric effect and photoelectrons are generated, so as to convert the low-energy radiation image input to it. for electronic images. The process of converting a radiation image into an optoelectronic image (ie photon-electron conversion) is achieved thereby.
2. Electron acceleration and focusing
The main function of the electron optical system is to accelerate the photoelectrons and gather them on the image plane. The main electronic optical systems are: electrostatic system and electromagnetic composite system. The former relies on the acceleration and focusing of the electrostatic field; the latter relies on the acceleration of the electric field and the focusing of the magnetic field. Because of the complex structure of the composite system, the electrostatic system is mostly used. The photoelectrons emitted from the photocathode are energized by a specific electrostatic field and accelerated and focused onto the phosphor screen.
3. Electron-photon conversion
Converts optoelectronic images into visible optical images using fluorescent screens. The kinetic energy of the photoelectricity is converted into light energy through the luminescent material on the fluorescent screen. After high-speed electrons bombard the surface of the phosphor screen, an enhanced visible image of the target corresponding to the incident weak light image is emitted to realize electron-photon conversion. In the end, the originally weak or invisible light signal becomes a strong visible light signal.

The role of low-light image intensifiers
Night vision technology is mainly represented by low-light night vision technology and infrared night vision technology. The advantages of infrared night vision technology are high sensitivity, long range, and the ability to penetrate smoke, dust and fog to observe the target, but the volume and weight are relatively large, and it is mainly used in vehicle, airborne and shipborne remote applications. Short-range night observation and aiming shooting at a distance of tens of meters to hundreds of meters are mainly solved by low-light night vision technology. In recent years, although low-light viewing technology has faced the challenge of infrared night vision technology, it still has obvious advantages in performance and cost.
Although the low-light night vision equipment has a relatively short working distance, it has high imaging resolution, and the image is similar to the visible light image, which is in line with the observation habits of the human eye and facilitates target recognition. Based on these factors, low-light night vision equipment will still have an irreplaceable role in the future.
The core of low-light night vision equipment is the low-light image intensifier. The low-light image intensifier can convert the scene illuminated by weak light into a visible light image through the photoelectric conversion of the photocathode, the multiplication of the electronic lens and the electro-optical conversion of the fluorescent screen. Low-light image intensifiers mainly work in the visible and near-infrared bands. In order to better adapt to the needs of the battlefield, people are developing a new generation of high-performance low-light image intensifiers that can be observed at longer distances, higher sensitivity, and lower illmination.
The development trend of low-light image intensifier
1. Continue to develop in the direction of high-sensitivity cathodes
The cathode sensitivity of the third-generation low-light image intensifier has now reached 2000μm/lm, and on this basis, it will develop in the direction of 3000μm/lm, reported in France. The transmission sensitivity of the multi-alkali photocathode optimized by program control can reach 800μm/lm, The Russians believe that the transmission sensitivity limit of the S-type multi-alkali photocathode is 1500 μm/lm. This shows that the S-type multi-alkali photocathode still has several great potentials to be tapped. It is expected to reach 800 to 1200 μm/lm in the image tube in the future.

2. Continue to develop in the direction of photocathodes extending to blue light and near-infrared
The research ZD of photocathode of low-light image intensifier is mainly developed in two directions. One is to study blue light extended (<550nm) GaAs negative electron affinity photocathode suitable for detection and identification in desert areas and underwater. Due to the strong infrared radiation in the sky, a photocathode extending from the near-infrared is developed.
3. Continue to improve the performance of microchannel plates
The all-weather war under modern high-tech conditions has higher and higher performance requirements for night vision devices, and correspondingly, the performance requirements for the micro-channel plate of the low-light image intensifier are also constantly improving. The general trend is high gain, low noise, and long life. , High resolution. The resolution of the microchannel plate depends on the aperture of the channel and the ZX distance of the channel. The smaller the channel, the smaller the ZX distance of the channel, and the higher the resolution.
4. Continue to develop in the direction of high transfer function and high resolution
Low-light image intensifiers will continue to enhance research to achieve high transfer function and high-resolution observations. For example, optimize the design of the whole machine and the image tube, adopt higher-performance fiber optic panels, micro-channel plates and fluorescent screens, shorten the distance between the micro-channel plate and the fluorescent screen, and develop new tube types. The fourth-generation low-light image intensifier developed by the American ITT company can improve its resolution to 90 line pairs/mm (the standard third-generation tube is 36 line pairs/mm). In the future, the resolution of low-light image enhancement is expected to reach 80 to 100 line pairs/mm.
Understanding Night Vision and Thermal Imaging Optics
Both night vision and thermal imaging optics allow you to see in the dark. They're helpful for a wide range of activities including night hunting, surveillance, wildlife observation, navigation, stargazing, and practicing tactical scenarios. Understanding which night vision optics you'll need can help you improve your efficiency in these activities.
Which Night Vision Optics Do You Need?
Choosing night vision equipment depends on your intended application. With night vision monoculars, you get a compact, lightweight design that makes the device very versatile. You can mount some models directly on weapons and use them as night vision riflescopes. Unlike monoculars, night vision goggles have no magnification, but they allow you to view objects with both of your eyes, giving you better depth perception and judgment of distances. Additionally, you can head-mount them, making them a handy and ideal choice for night navigation. Night vision binoculars come with two eyepieces with powerful, built-in magnification. Thus, if your main activity involves long-range night viewing, then these binoculars are the most suitable choice.
How Thermal Imaging Optics Work
Thermal imaging optics use sensors that detect heat (or radiation) to help you see in the dark. The radiation of the electromagnetic spectrum has varying wavelengths, which you can interpret as color. Short wavelengths have a high amount of energy and you can see them as lighter colors, while long wavelengths have a low amount of energy and you view them as darker colors. Through thermal vision goggles or scopes, you see different shades of colors to determine objects. They're especially useful for surveillance, energy auditing, wildlife spotting, and firefighting.
Night Vision Accessories
Depending on your application, you'll need some night vision accessory kits to improve the performance of your night vision devices. To conveniently mount night vision optics on your head, you'll have to shop for night vision headgear such as head mounts, head mount adapters, and quick release systems. If you're planning to use night vision scopes with your camera, you'll need camera adapters for your specific camera model. With night vision filters, you can eliminate visible light and glare for covert use of your optics.
Whether you're looking for night vision bi-oculars or night vision telescopes, you can be sure to find what you need with B&H Photo and Video's wide assortment of night and thermal vision optics and accessories.
 tel
tel



